Imagine regrowing your own hair, not just moving it around. That’s the big promise behind hair cloning, also known as hair multiplication.
Unlike traditional transplants that shift follicles from one area to another, this method takes a small sample of your healthy hair follicles, multiplies them in a lab, and reimplants them where you need new growth.
Sounds futuristic? It kind of is. But scientists are already making real progress.
The exciting part? This could solve the biggest issue with hair transplants: limited donor hair.
If hair cloning works on a large scale, we might one day have an endless supply of your own hair to work with, no scars, no shortage, just real regeneration.
Why Hair Cloning Is Generating So Much Buzz in 2025
Hair cloning isn’t just another cosmetic trend; it’s capturing the attention of scientists, biotech companies, and people struggling with hair loss worldwide.
Unlike conventional treatments that rearrange existing follicles, this technique promises something revolutionary: the ability to grow brand-new hair follicles from your own cells.
In a field where options have remained fairly static for years, this potential shift has sparked hope for a future where hair loss is no longer a permanent condition.
How Does Hair Cloning Work? The 3-Step Scientific Process
Hair cloning follows a carefully structured scientific approach. It involves working with specialized cells found at the base of healthy hair follicles, dermal papilla cells, which play a crucial role in hair growth and cycling.
Step 1: Cell Extraction
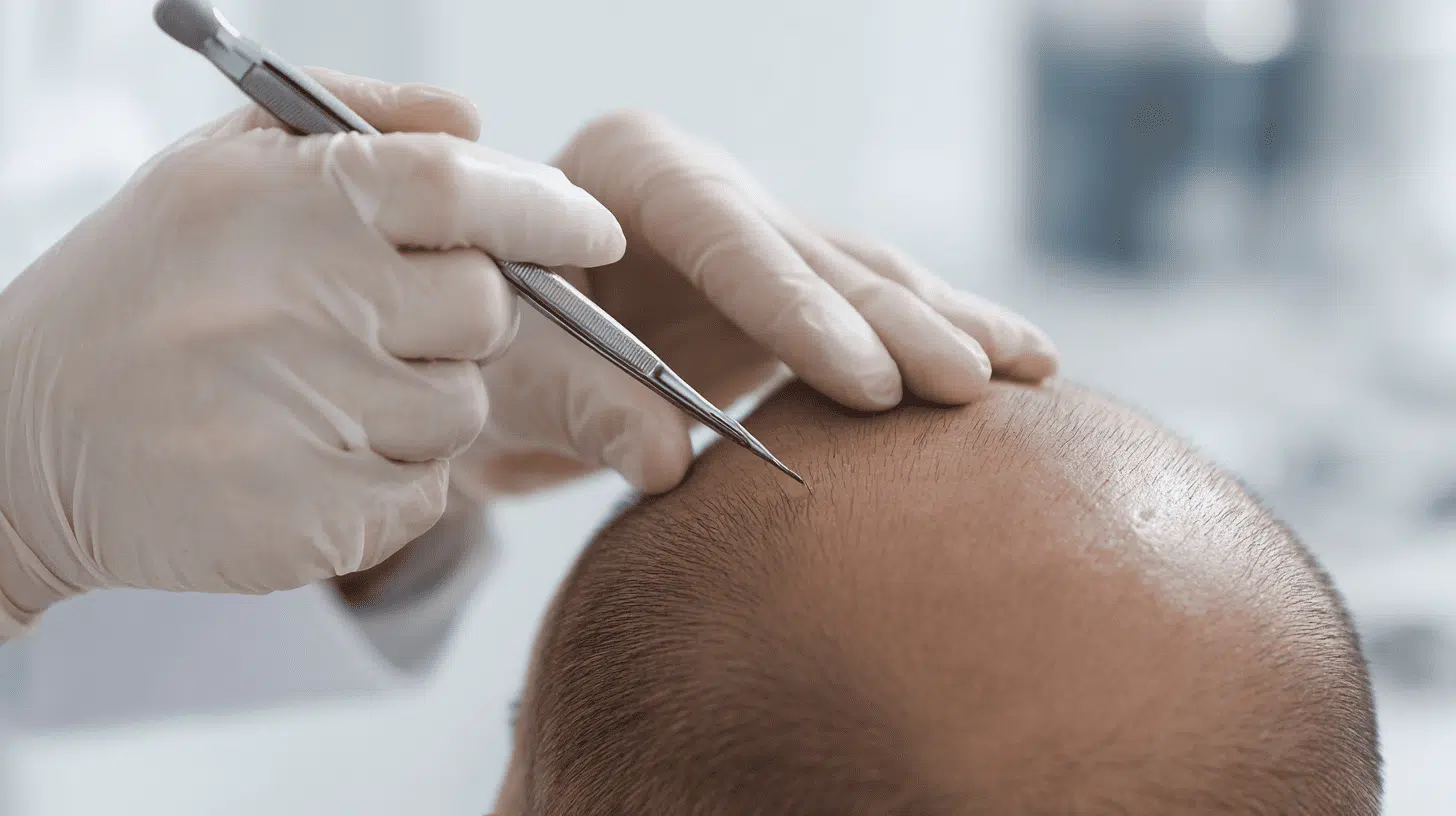
A tiny scalp biopsy is taken to isolate dermal papilla cells from healthy, active hair follicles. These specialized cells are key to hair growth and regeneration.
The extraction process is minimally invasive and carefully targets follicles that show strong growth potential, ensuring the best source for future multiplication.
Step 2: Cell Culturing & Multiplication

The extracted dermal papilla cells are carefully nurtured in lab settings using growth factors, oxygen, and nutrients. These conditions help the cells multiply while preserving their hair-regenerating abilities.
Controlled environments ensure consistency, safety, and viability, laying the groundwork for future implantation into areas experiencing hair thinning or loss.
Step 3: Reimplantation
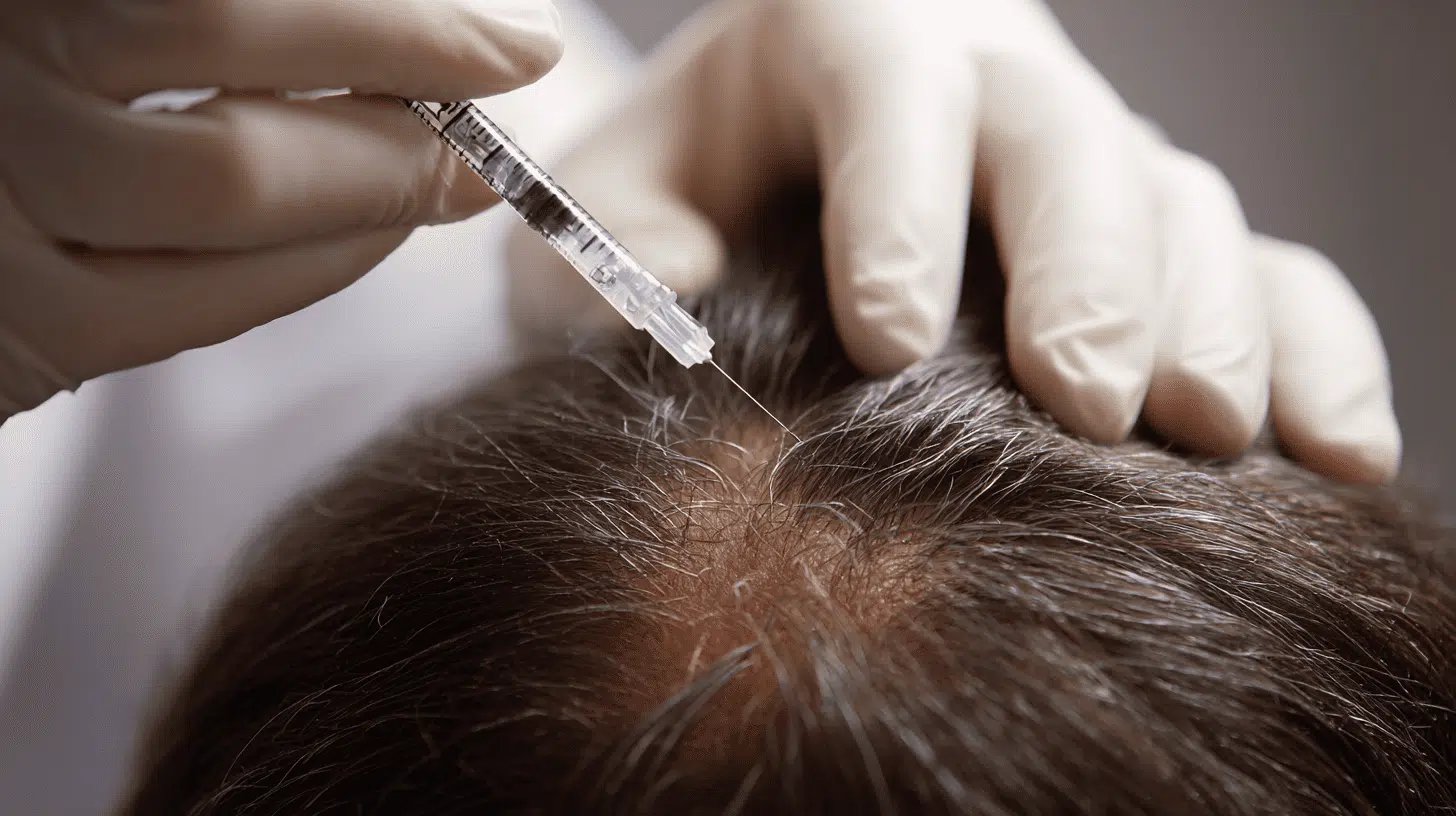
Once a sufficient number of healthy cells are cultured, they’re injected into thinning or balding areas of the scalp. These cells stimulate the surrounding tissue to regenerate new hair follicles naturally.
The goal is to restore consistent hair growth that blends seamlessly with existing strands, without requiring donor grafts.
Latest Advances in Hair Cloning Research
Recent developments in hair cloning are bringing us closer to a future where regenerating your own hair might actually be possible.
- Animal Models: Studies in mice have successfully regenerated full hair follicles using cultured cells, showing early promise.
- Clinical Trials: Companies like HairClone (UK) and Stemson Therapeutics (U.S.) are pioneering early human trials, including follicle banking and bioengineered grafts.
- 3D Bioprinting: Some research teams are exploring 3D bioprinting of follicle structures to improve control, viability, and scalability.
While these breakthroughs are promising, more clinical trials and real-world testing are needed before hair cloning becomes a routine option in hair restoration clinics.
Challenges & Limitations
Hair cloning holds exciting potential, but getting it from the lab to your dermatologist’s office isn’t as easy as it sounds.
- Cultured follicle cells may lose their ability to grow hair if not handled correctly.
- It’s hard to consistently replicate natural hair direction, density, and survival rates.
- Even with your own cells, immune reactions or poor integration can occur.
- No FDA-approved protocols exist yet, making regulatory approval a major hurdle.
- Current techniques are costly, complex, and not yet practical for mass use.
- Scaling production while maintaining quality remains an unsolved challenge.
Until these challenges are resolved, from safety and regulation to real-world results, hair cloning remains a promising concept still waiting for its commercial breakthrough.
How Hair Cloning Compares to Traditional Transplants
Curious how future-forward hair cloning stacks up against time-tested transplant techniques? Let’s break down the key differences side by side.
| Aspect | Traditional Hair Transplants (FUE/FUT) | Hair Cloning |
|---|---|---|
| Donor Supply | Limited by existing follicles | Potentially unlimited new follicles |
| Procedure | Relocates follicles from dense to thin areas | Lab-grown cells implanted into the scalp |
| Availability | Widely available today | Experimental trials are ongoing |
| Results | Proven, consistent | Promising, but not proven in humans yet |
| Cost (U.S.) | $2,000 – $5,000+ | Likely higher initially, unknown range |
| Recovery Time | Moderate (1–2 weeks) | Unknown, likely minimal |
| Long-Term Potential | Limited to the current follicle supply | Could offer self-renewing, unlimited hair |
While traditional transplants remain the go-to solution today, hair cloning may soon offer a less invasive, donor-free option, if science catches up.
When Will Hair Cloning Become a Reality?
As of 2025, hair cloning isn’t available to the public yet, but it’s getting closer.
Many researchers believe we could see it in clinics within the next 5 to 10 years, depending on how fast progress continues.
A few key things need to happen first: scientists must perfect how to grow and implant viable hair follicles, regulatory bodies like the FDA and MHRA need to approve procedures, and the entire process must become affordable and scalable for everyday use.
In the meantime, hair follicle banking is a promising first step. Clinics like HairClone already allow people to store their healthy follicles for use in future treatments once cloning becomes viable.
Additional Innovations Complementing Hair Cloning
While we wait for hair cloning to mature, several complementary technologies are reshaping the hair restoration landscape:
- Stem cell therapy aims to reactivate dormant follicles and enhance scalp health through regenerative injections.
- Exosome therapy, derived from stem cells, helps stimulate follicle repair and growth by delivering growth signals to target areas.
- Robotic-assisted hair transplantation is becoming more precise, allowing for better graft placement and less manual error.
These advancements could be used in tandem with hair cloning to enhance effectiveness and tailor treatment to individual needs.
Wrapping it Up
Hair cloning has the potential to completely shift how we treat hair loss. Instead of relocating existing follicles, this technique could one day create an endless supply using your own cells.
That’s a game-changer for people with limited donor hair or extensive thinning.
As of 2025, it’s still in the experimental phase, but research, clinical trials, and follicle banking programs are making steady progress. If successful, hair cloning could mean natural results without surgery or scars.
For now, traditional methods like FUE and FUT remain the most reliable options. But the future of hair restoration may soon be more personalized, regenerative, and limitless than ever imagined.
















